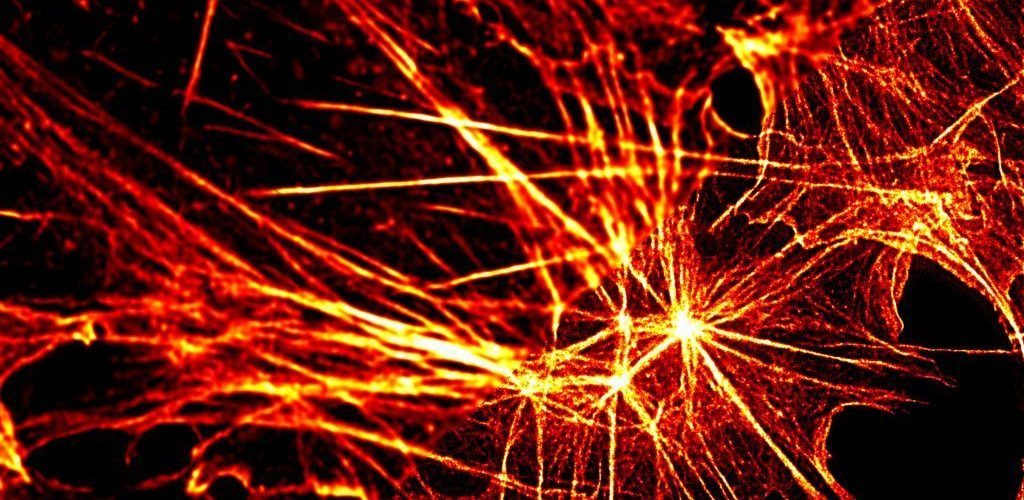
STED microscopy is widely used to study luminescent samples with a high spatial resolution far below the diffraction barrier in the fields of biology, medicine as well as materials science. Therefore, in a confocal laser scanning microscope, the sample is excited with a diffraction-limited, pulsed laser, followed by a doughnut-shaped second laser pulse which is red-shifted with regard to the emission spectrum of the chromophore.
This document provides a quick overview of the STED technique introduced by Stefan W. Hell in 1994. NKT Photonics’ SuperK and KATANA HP lasers are a perfect combination to realize flexible pulsed excitation as well as synchronized depletion within the visible and near-infrared range.
STED illumination



This leads to a depletion of the outer ring of the confocal excitation volume. The remaining fluorescence after the depletion pulse is therefore only emitted from a shrunk region in the center of the excitation volume.

The SuperK Supercontinuum lasers deliver a continuous spectrum over the visible (Vis) and near-infrared (nIR) range, with excellent single-mode beam profile (M2 < 1.1) and picosecond (ps) pulse duration. In combination with our filter technology, it can be transformed into a tunable laser source, allowing optimized excitation of every chromophore absorbing in the Vis and nIR regions.
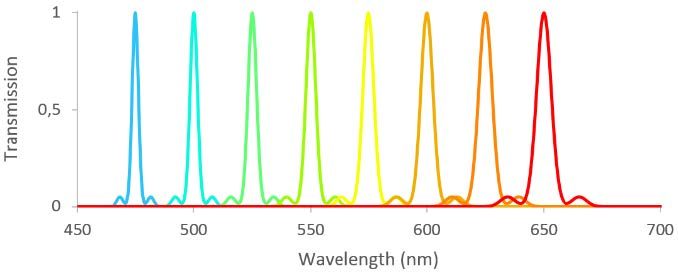
The KATANA HP lasers are available at various wavelengths within the Vis-nIR and offer high pulse energy at ps pulse duration making them ideal for STED depletion.

available wavelength for KATANA HP lasers (red).
In addition to using the proper combination of wavelengths and laser power levels, in STED microscopy it is also crucial to precisely adjust the excitation and depletion laser pulses, to synchronize for efficient depletion of the excited chromophores at the beginning of each fluorescence cycle.
NKT Photonics’ mode-locked Supercontinuum lasers are equipped with a NIM trigger output and built-in adjustable trigger delay as a standard feature. The KATANA HP lasers can run as a slave on external trigger input, which allows for simple software-controlled adjustment of the excitation and depletion pulses.
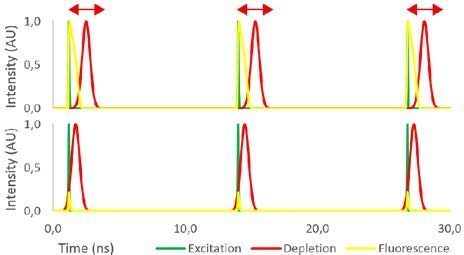
optimize depletion for the best resolution.
In the experiment, the resolution is mainly limited by the photophysics of the chromophore used. That is why new fluorescent labels are developed rapidly. Consequently, the flexibility of a Supercontinuum laser to freely choose the excitation wavelength helps to prepare for upcoming labels in the VIS-nIR.
The combination of the SuperK platform with the KATANA HP laser family becomes a turnkey solution for the most flexible and modular implementation of STED microscopy on the market successfully proven through multiple installations worldwide.
Suitable hardware configuration for STED microscopy:
Supercontinuum excitation:
Pulsed depletion:
- Onefive KATANA 08 HP (e.g. 775 nm depletion)
- Onefive KATANA 06 HP (e.g. 592 nm depletion)





