Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT) enables cross-sectional or 3D imaging of the subject under investigation. This is a huge advantage compared to alternative microscopy techniques where you can only investigate the surface or shallow layers of the subject.
Cross-sectional or 3D imaging is relevant for various applications, ranging from the analysis of tissue in medical applications to visualization of sub-micron structures in manufacturing.
The OCT principle for imaging was first demonstrated in 1991 by Professor Huang et al.. A very thorough description of principles and applications has been provided by Professor Drexler from the Medical University Vienna and Professor Fujimoto from MIT in “Optical Coherence Tomography: Technology and Applications”.
Over the last 20 years, OCT has become an essential imaging tool in ophthalmology with particular emphasis on detailed analysis of the retina and the surrounding tissue.
OCT applications are, however, not limited to ophthalmology. An increasing amount of research is made in OCT outside the ophthalmology field.
The SuperK supercontinuum lasers offer several key parameters relevant for UHR-OCT:
- Extreme optical bandwidths
- Excellent spatial coherence
- High optical power density
The number of OCT applications using SuperK sources is increasing rapidly.
OCT in a nutshell
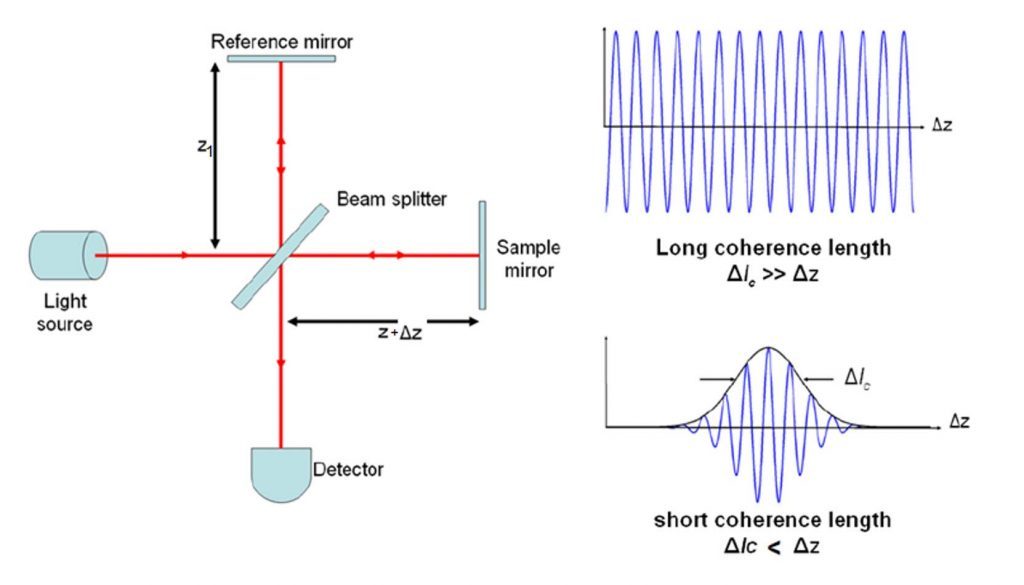
OCT is based on interferometry. Light from one arm is reflected or scattered off the subject under investigation and interferes with light from a reference arm.
The light from both arms originates from the same light source. The two light beams will interfere if the difference in the path lengths is within the coherence length of the optical signal.
This coherence gating lets the detection system to discriminate between reflections from closely spaced reflectors enabling high-resolution imaging.
The sensitivity of OCT is so high it can detect even the weak signals from sub-surface reflections. In this way, cross-sectional imaging can be realized – much like ultrasound – but with a much higher resolution. Image depths of several mm into the tissue can be achieved.
Practical realizations of OCT
There are different practical realizations of OCT:
- Time-domain OCT (TD-OCT): The reference mirror is moving hence enabling coherence gating at different depths in the sample arm. This was the very first realization of OTC and it is still relevant e.g. for Full-Field OCT where the interference pattern for a full 2-dimensional array is detected simultaneously by a 2D detector array (e.g. CCD or CMOS).
- Spectral-domain OCT (SD-OCT): Also known as Fourier-domain OCT (FD-OCT) where the reference mirror is fixed and the interference pattern is detected spectrally and converted to spatial information by the Fourier transformation.
- Spectrometer based OCT (Sp-OCT): A broadband source (such as a SuperK source) is used to generate the interference spectrum which is detected with a high-speed spectrometer, typically with several thousand pixels and sub-nm optical resolution.
- Swept-source OCT (SS-OCT): A tunable source is rapidly scanning the relevant spectral range. The spectral response of the interferometer is detected by a single or a balanced detector.
Each of these techniques has different advantages and disadvantages, which make them more or less relevant for certain applications.
SuperK sources can be used in all of the above realizations. For SS-OCT, a SuperK can be used with a rapidly scanning bandpass filter to effectively sweep the center wavelength. Most SuperK sources, however, have been applied to SD-OCT based on spectrometer detection (Sp-OCT).
Low noise ensures high-contrast images
The SuperK FIANIUM supercontinuum laser series has the lowest noise on the market. Optimized for low-noise performance, it gives high-contrast low-noise images in OCT systems. Its performance matches that of bulky Ti:Sapphire lasers.
Below are shown two OCT images of a human eye. The image on the right is recorded using a SuperK EXTREME OCT source, while the image on the left is obtained using a Ti:Sapphire laser. Both images are recorded by Angelika Unterhuber from Prof. Dr. Wolfgang Drexlers group at Medical University Vienna.

How others have used supercontinuum white light lasers for OCT
Papers describing OCT using a SuperK supercontinuum source:
- Shot-noise limited, supercontinuum-based optical coherence tomography by Shreesha Rao D. S., Mikkel Jensen, Lars Grüner-Nielsen, Jesper Toft Olsen, Peter Heiduschka, Björn Kemper, Jürgen Schnekenburger, Martin Glud, Mette Mogensen, Niels Møller Israelsen, and Ole Bang, published in Light: Science & Applications, 10, Article number: 133 , 2021.
- Revealing brain pathologies with multimodal visible light optical coherence microscopy and fluorescence imaging by Antonia Lichtenegger, Johanna Gesperger, Barbara Kiesel, Martina Muck, Pablo Eugui, Danielle J. Harper, Matthias Salas, Marco Augustin, Conrad W. Merkle, Christoph K. Hitzenberger, Georg Widhalm, Adelheid Wöhrer, and Bernhard Baumann, published in Journal of Biomedical Optics, Vol. 24, Issue 6, 2019.
- Speckle reduction in visible-light optical coherence tomography using scan modulation by Ian Rubinoff, Lisa Beckmann, Yuanbo Wang, Amani A. Fawzi, Xiaorong Liu, Jenna Tauber, Katie Jones, Hiroshi Ishikawa, Joel S. Schuman, Roman Kuranov, Hao F. Zhang, published in Neurophotonics Vol. 6, Issue 4, 2019.
- Longitudinal deep-brain imaging in mouse using visible-light optical coherence tomography through chronic microprism cranial window by Lisa Beckmann, Xian Zhang, Neil A. Nadkarni, Zhen Cai, Ayush Batra, David P. Sullivan, William A. Muller, Cheng Sun, Roman Kuranov, and Hao F. Zhang Published in Biomedical Optics Express, Vol. 10, Issue 10, 2019.
- Hyperspectral optical coherence tomography for in vivo visualization of melanin in the retinal pigment epithelium by Danielle J. Harper, Thomas Konegger, Marco Augustin, Kornelia Schützenberger, Pablo Eugui, Antonia Lichtenegger, Conrad W. Merkle, Christoph K. Hitzenberger, Martin Glösmann, and Bernhard Baumann, published in Journal of Biophotonics, 2019.
- Real-time high-resolution mid-infrared optical coherence tomography by Niels M. Israelsen, Christian R. Petersen, Ajanta Barh, Deepak Jain, Mikkel Jensen, Günther Hannesschläger, Peter Tidemand-Lichtenberg, Christian Pedersen, Adrian Podoleanu and Ole Bang published in Nature Light: Science & Applications 8, article 11, 2019.
- Noise of supercontinuum sources in spectral domain optical coherence tomography by Mikkel Jensen, Iván Bravo Gonzalo, Rasmus Dybbro Engelsholm, Michael Maria, Niels Møller Israelsen, Adrian Podoleanu, and Ole Bang published in Journal of the Optical Society of America B, 36(2):A154, Feb. 2019.
- Potential of contrast agents to enhance in vivo confocal microscopy and optical coherence tomography in dermatology: A review by Hans C. Ring, Niels M. Israelsen, Ole Bang, Merete Haedersdal, and Mette Mogensen published in Journal of Biophotonics, Vol. 12, Issue 6, March 2019.
- VIS-OCT Opens Eyes to New Approaches – Attention and investment could revolutionize applications in visioning and treatment of eye-related diseases By Hao F. Zhang, Northwestern University and Kieren Patel, Opticent Health, published in BioPhotonics, Sep. 2019.
- Line-field confocal optical coherence tomography for high-resolution noninvasive imaging of skin tumors by Arnaud Dubois, Olivier Levecq, Hicham Azimani, David Siret, Anaïs Barut, Mariano Suppa, Véronique del Marmol, Josep Malvehy, Elisa Cinotti, Pietro Rubegni, Jean-Luc Perrot published in Journal of Biomedical Optics, Vol. 23, Issue 10, 2018.
- The value of ultrahigh resolution OCT in dermatology – delineating the dermo-epidermal junction, capillaries in the dermal papillae and vellus hairs by Niels Møller Israelsen, Michael Maria, Mette Mogensen, Sophie Bojesen, Mikkel Jensen, Merete Haedersdal, Adrian Podoleanu, and Ole Bang, published in Biomedical Optics Express, Vol. 9, Issue 5, 2018.
- All-depth dispersion cancellation in spectral domain optical coherence tomography using numerical intensity correlations by Mikkel Jensen, Niels Møller Israelsen, Michael Maria, Thomas Feuchter, Adrian Podoleanu, and Ole Bang published in Scientific Reports 8, Article 9170, 2018.
- Two optical coherence tomography systems detect topical gold nanoshells in hair follicles, sweat ducts and measure epidermis by Mette Mogensen, Sophie Bojesen, Niels Møller Israelsen, Michael Maria, Mikkel Jensen, Adrian Podoleanu, Ole Bang, Merete Haedersdal published in Journal of Biophotonics, Vol. 11, Issue 9, 2018.
- Recovering distance information in spectral domain interferometry by Adrian Bradu, Niels Møller Israelsen, Michael Maria, Manuel J. Marques, Sylvain Rivet, Thomas Feuchter, Ole Bang, and Adrian Podoleanu, published in Scientific Reports 8, Article 15445, 2018.
- Assessment of pathological features in Alzheimer’s disease brain tissue with a large field-of-view visible-light optical coherence microscope by Antonia Lichtenegger, Martina Muck, Pablo Eugui, Danielle J. Harper, Marco Augustin, Konrad Leskovar, Christoph K. Hitzenberger, Adelheid Woehrer, Bernhard Baumann, published in Neurophotonics, Vol 5, Issue 3, 2018.
- White light polarization sensitive optical coherence tomography for sub-micron axial resolution and spectroscopic contrast in the murine retina by Danielle J. Harper, Marco Augustin, Antonia Lichtenegger, Pablo Eugui, Carlos Reyes, Martin Glösmann, Christoph K. Hitzenberger, and Bernhard Baumann published in Biomedical Optics Express, Vol 9, Issue 5, 2018.
- Spectroscopic imaging with spectral domain visible light optical coherence microscopy in Alzheimer’s disease brain samples by Antonia Lichtenegger, Danielle J. Harper, Marco Augustin, Pablo Eugui, Martina Muck, Johanna Gesperger, Christoph K. Hitzenberger, Adelheid Woehrer, and Bernhard Baumann published in Biomedical Optics Express, Vol 8, Issue 9, 2017.
- Q-switch-pumped supercontinuum for ultra-high resolution optical coherence tomography by Michael Maria, Ivan Bravo Gonzalo, Thomas Feuchter, Mark Denninger, Peter M. Moselund, Lasse Leick, Ole Bang, and Adrian Podoleanu, published in Optics Letters, Vol. 42, Issue 22, 2017.
- Simultaneous optical coherence tomography and lipofuscin autofluorescence imaging of the retina with a single broadband light source at 480nm by Minshan Jiang, Tan Liu, Xiaojing Liu, and Shuliang Jiao, published in Biomedical Optics Express, Vol. 5, Issue 12, pp. 4242-4248, 2014.
- All fiber ultra-high resolution Fourier domain optical coherence tomography for old master paintings by Chi Shing Cheung, Marika Spring, and Haida Liang, published in Optics Express, Vol 23, Issue 8, 2015.
- Feasibility of the Assessment of Cholesterol Crystals in Human Macrophages Using Micro Optical Coherence Tomography by Manabu Kashiwagi, Linbo Liu, Kengyeh K. Chu, Chen-Hsin Sun, Atsushi Tanaka, Joseph A. Gardecki, Guillermo J. Tearney, published in PLoS ONE 9(7), 2014.
- Ultra-high-resolution and ultra-high-sensitive optical micro-angiography based on supercontinuum light source by Zhongwei Zhi, Lin An, Jia Qin, and Ruikang K. Wang, published in SPIE proceedings, Vol. 7889, 2011.
- Non-invasive imaging and monitoring of rodent retina using simultaneous dual-band optical coherence tomography by Peter Cimalla, Anke Burkhardt, Julia Walther, Aline Hoefer, Dierk Wittig, Richard Funk, and Edmund Koch, published in SPIE proceedings Vol. 7889, 2011.
- Phase-dispersion light scattering for quantitative size-imaging of spherical scatterers by Tasshi Dennis, Shellee D. Dyer, and Andrew Dienstfrey
- Shear flow-induced optical inhomogeneity of blood assessed in vivo and in vitro by spectral domain optical coherence tomography in the 1.3 μm wavelength range by Peter Cimalla, Julia Walther, Matthaeus Mittasch and Edmund Koch, published in Journal of Biomedical Optics, Vol 16. Issue 11, 2011.
- Simultaneous dual-band optical coherence tomography in the spectral domain for high resolution in vivo imaging by Peter Cimalla, Julia Walther, Mirko Mehner, Maximiliano Cuevas, and Edmund Koch, published in Optics Express, Vol. 17, Issue 22, pp. 19486-19500, 2009.
- Visible-light OCT spectrometer for microvascular oximetry by Gangnus, Sergei V., and Stephen J. Matcher, Proceedings of SPIE, the International Society for Optical Engineering. Society of Photo-Optical Instrumentation Engineers, 2008.
ARTICLES AND BACKGROUND INFO
- Article by Adam Wax, published in the Nature Photonics: Molecular imaging true-colour spectroscopic optical coherence tomography
- Article by Adam Wax, published in the Biomedical Optics Express: Multispectral nanoparticle contrast agents for true-color spectroscopic optical coherence tomography
- Paper by Adam Wax: Quantitative phase microscopy with off-axis optical coherence tomography
- Article by Chao Zhou, published in the Biomedical Optics Express: Characterization of eosinophilic esophagitis murine models using optical coherence tomography
- Article by Chao Zhou, published in the Biomedical Optics: Label-free evaluation of angiogenic sprouting in micro-engineered devices using ultrahigh-resolution optical coherence microscopy
- Article by Jannick P. Rolland in the Biomedical Optics: Measurement of a multi-layered tear film phantom using optical coherence tomography and statistical decision theory
- Article by F. Li, Y. Song, A. Dryer, W. Cogguillo, Y. Berdichevsky, C. Zhou, published in the Neurophotonics: Nondestructive evaluation of progressive neuronal changes in organotypic rat hippocampal slice cultures using ultrahigh-resolution optical coherence microscopy