See what’s invisible to the naked eye
With hyperspectral imaging, you can analyze and sort any material: See what’s under the skin of an apple, detect fungicides, or analyze the composition of fish or meat. In short, get a fingerprint of your sample.
For this, you need a bright, stable, and focused light source to make reliable, repeatable measurements. Compared to incandescent lamps, a SuperK laser has many advantages.
Incandescent lamps develop heat. They have a short lifetime and poor brightness. A SuperK laser delivers focused light and offers better thermal management. It has a long lifetime and a high brightness which give you a high resolution and a short sampling time.

Get enough light
Hyperspectral imaging is an emerging imaging technique in many applications, from food and recycling sorting to medical imaging and semiconductor metrology. It can help you sort materials based on multiple spectral features. The image is made by recording individual pixels per nanometer and reconstructing them into a hyperspectral image.
In many applications, ambient light or incandescent lamps will not provide enough light. For high-performance systems, you need advanced light sources such as the SuperK lasers. Compared to other light sources, SuperK offers a higher resolution and better signal-to-noise ratio resulting in higher throughput.

Get additional information from the SWIR spectrum
When talking about hyperspectral imaging, we must mention the short-wave infrared spectrum, SWIR. Using light in the 1700 – 2500 nm spectrum lets you see things that are invisible when using other wavelengths. This is relevant, e.g., for the sorting of minerals.
It is difficult to find appropriate light sources that cover the SWIR spectrum. LEDs and incandescent light bulbs do not cover these wavelengths, and halogen lamps have limited power in the SWIR range. Conventional lasers can give light at discrete wavelengths, but only a supercontinuum laser, such as the SuperK laser, offers light in the 1700 – 2500 nm spectrum.
A SuperK laser gives you single-mode light that can be focused into a small spot or a narrow line and still keep its high brightness.

Analyze and sort anything
A hyperspectral imaging set-up lets you analyze and sort anything. You can sort general waste and different plastic types, classify textiles, determine mineral composition, detect food adulteration, and much more…
Food sorting is getting a lot of attention at the moment. If you work with meats, produce, or processed foods, a hyperspectral imaging set-up lets you look for, e.g., bruising, ripening, pesticide residues, skin defects, internal defects, sugar content, protein, fungicide, fat, salt, moisture, blood, bones, freshness, and meat structure.

Different sorting techniques see different things
Scan types
In the production line, you can use different sorting techniques:
- Point scan
- Line scan (or push broom)
- Wavelength scan
- Snapshot imaging
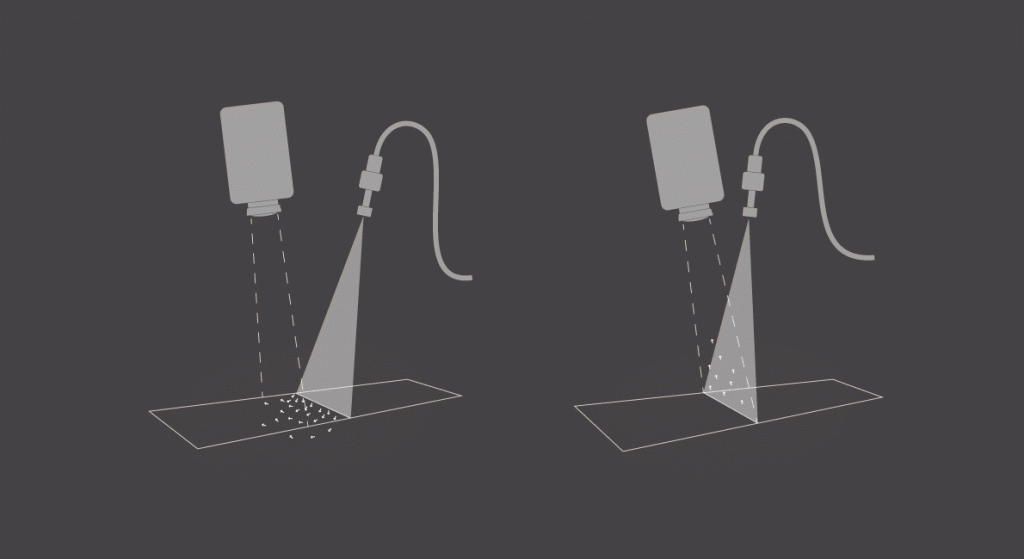
Laser light can be tightly focused, so the SuperK laser is especially well-suited for point scan, where you need a small light spot, and line scan, where you need a narrow line of light.
Reflectance, transmittance, or scattering
When you work with point or line scanning you can apply three sorting techniques, depending on what you want to see.
- Reflectance-based measurements are employed to study the surface properties of the samples.
- Transmission-based measurements are employed to study the properties of the bulk of the materials deeper within the samples.
- Trans-interactance measurements are typically used to study the light interaction of the materials in a shallow volume of samples. This scattering measurement method is less sensitive to the surface properties of the sample.
Our SuperK laser can be used as the light source for hyperspectral imaging in chute feeds, conveyor belts, or channels.
A wide and stable spectrum
To make reliable, repeatable measurements, your light source must have high brightness and a broad, flat, and stable spectrum.
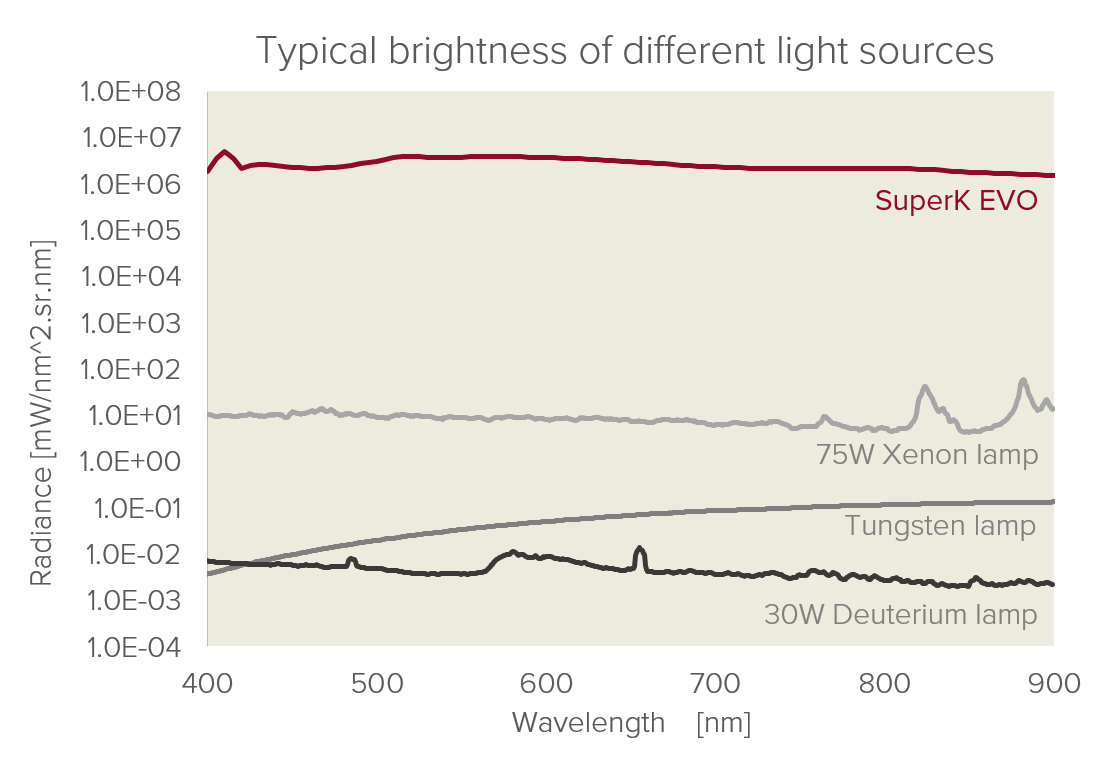
Unlike, e.g., LEDs, SuperK lasers have no wavelength peaks, and because the spectrum is flat compared to lamps, the signal-to-noise ratio is easy to manage. The SuperK covers the visible, nIR, and SWIR wavelengths from 400 – 2500 nm.
Ultimate brightness
With a SuperK, you can focus the perfectly collimated output beam without losing intensity. Its light is 100 times brighter than any comparative incoherent light source.
You get more signal – even when measuring diffuse, opaque, and scattering materials. The high brightness gives you a high sorting speed.
Install and forget!
At the heart of the SuperK, you will find our renowned Photonic Crystal Fiber (PCF) technology. This solid-state, all-fiber architecture ensures a reliable 24/7 operation and runs maintenance-free for 10,000 hours – the longest in the market.
Intended for industrial use, the SuperK is easy to mount and handle due to its rugged and compact design. Reliability, quality, and performance are ensured through the DIN ISO 9000 certified processes.

Light sources pros & cons
All light sources have pros and cons. Let’s sum them up.

Read the application note if you want to know how to use a SuperK EVO for hyperspectral imaging.


